Asthma Exacerbation in Adults – Diagnosis
Cardinal Presentations / Presenting Problems, Inflammatory, Respiratory
Context
- 8% of Canadians over the age of 18 have asthma.
- Onset is less common with increasing age.
- Typically presents with dyspnea, cough, wheezing and chest tightness.
- Wheezes are generally widespread, expiratory, high-pitched and musical.
- Common exacerbating factors include:
- Viral respiratory infections,
- Allergen/irritant exposures,
- Poor adherence with controller medications.
- Severe cases can be fatal.
Diagnostic Process
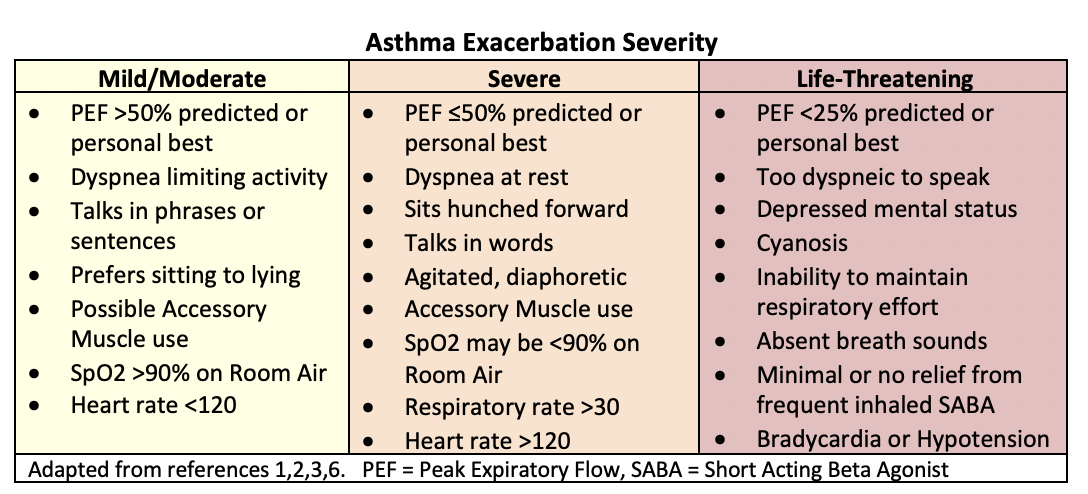
- While initiating therapy, measure SpO2 and Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF).
- Assess severity to guide management.
- Consider alternate or comorbid conditions.
- Pulmonary Function Testing
- Peak expiratory flow (PEF) is mainstay of objective testing.
- If possible, perform before treatment.
- Inability to perform this test in a cooperative patient = severe obstruction.
- Normal PEF values depend on gender, height and age. However, in general PEF > 300 L/min = mild/moderate exacerbation.
- Alternative or comorbid diagnoses:
- COPD Exacerbation.
- Heart failure.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Pneumothorax.
- Pneumonia.
- Anaphylaxis.
- Foreign body:
- Poor airway protection, unilateral/localized wheeze.
- Investigations:
- Arterial Blood Gasses:
- Consider for severe exacerbations or in patients not improving.
- PaCO2>45mmHg or PaO2<60mmHg suggest respiratory failure.
- Chest Radiograph:
- For severe exacerbations or those requiring hospitalization.
- If there is suspicion of a comorbid process, or if diagnosis uncertain.
- Arterial Blood Gasses:
Quality Of Evidence?

High
We are highly confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. There is a wide range of studies included in the analyses with no major limitations, there is little variation between studies, and the summary estimate has a narrow confidence interval.
Moderate
We consider that the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. There are only a few studies and some have limitations but not major flaws, there are some variations between studies, or the confidence interval of the summary estimate is wide.
Low
When the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. The studies have major flaws, there is important variations between studies, of the confidence interval of the summary estimate is very wide.
Justification
Evidence comes from sources published within the last few years, including the 2019 GINA guidelines, which are in relative agreement about methods of recognizing and investigating asthma exacerbations.
Related Information
Reference List
Relevant Resources
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated Jun 09, 2020
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…


POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.